|
Collagen
膠原(膠原蛋白)
From Wikipedia, the free
encyclopedia(維基百科)
Translated By : The Analytical Based Development Center
Collagen /ˈkɒlədʒɨn/ is the main structural protein of
the various connective tissues in animals. As the main component of
connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals,[1] making up from 25% to 35% of the
whole-body protein content.
Collagen, in the form of elongated fibrils, is mostly found in fibrous
tissues such as tendons,
ligaments and skin. It is also abundant in corneas, cartilage, bones, blood
vessels, the gut, intervertebral discs and the dentin in teeth.[2]
In muscle tissue, it serves as a major component of the
endomysium. Collagen constitutes one to
two percent of muscle tissue, and accounts for 6% of the weight of strong,
tendinous muscles.[3] The fibroblast is the most common cell that creates
collagen.
膠原/kɒlədʒɨn/是動物裏各種結締組織的主要結構蛋白.
作為結締組織的主要成分,
它是哺乳動物裏最富的蛋白, [1]構成全身25%至35%的蛋白質含量.
膠原蛋白,
以其細長的纖維形式,
主要是在纖維組織如腱,
韌帶和皮膚中發現.
它在角膜,
軟骨,
骨,
血管,
內臟,
椎間盤和在牙齒牙質裏也是豐富的. [2]
在肌肉組織中,
它作為內膜的主要組成部分.
膠原構成1%到2%的的肌肉組織,
並且佔強壯的腱肌肉重量的6%. [3]
成纖維細胞是產生膠原最常見的細胞.
Gelatin, which is used in food and
industry, is collagen that has been irreversibly hydrolyzed. Collagen also has many medical
uses in treating complications of the bones and skin.
The name collagen comes from the Greek κολλα, kolla meaning "glue" and suffix -γέν, -gen denoting "producing."[4][5] This refers to the compound's early
use in the process of boiling the skin and
sinews of horses and
other animals to obtain glue.
明膠,
其用於食品和工業,
是已被不可逆地水解的膠原.
膠原蛋白在治療骨骼和皮膚的並發症也有很多醫療用途.
膠原蛋白名稱來源於希臘κολλα,
克拉(Kolla)意為 ”膠水”和字尾-γέν, -gen表示“生產.”[4] [5]
這是指該化合物早期以煮沸馬和其他動物的皮膚和鍵的程序,
以取得膠水的使用.
Contents內容
·
1 History and background歷史和背景
·
2 Chemistry
化學
·
3 Synthesis
合成
o
3.3 Synthetic pathogenesis合成的發病機制
·
4 Molecular structure分子結構
·
5 Types and associated disorders類型和相關疾病
·
6 Diseases個病
·
7 Characteristics特點
o
7.1 Uses用途
·
8 Medical uses醫療用途
o
8.1 Cardiac applications心臟應用
o
8.2 Type II collagen and rheumatoid arthritis II型膠原蛋白和類風濕關節炎
o
8.3 Hydrolyzed type II collagen and osteoarthritis水解II型膠原和骨關節炎
o
8.4 Cosmetic surgery整容手術
o
8.5 Bone grafts骨移植
o
8.6 Tissue regeneration組織再生
o
8.7 Reconstructive surgical uses重建手術用途
o
8.8 Wound care management uses傷口護理管理用途
·
9 See also參見
·
10 References參考
·
11 External links外部鏈接
History and background
歷史和背景
The molecular and packing structures of collagen have eluded scientists over
decades of research. The first evidence that it possesses a regular structure at
the molecular level was presented in the mid-1930s.[6][7] Since that time, many prominent
scholars, including Nobel laureates Crick, Pauling, Rich and Yonath, and others, including Brodsky, Berman, and Ramachandran, concentrated on the
conformation of the collagen monomer.
膠原蛋白的分子和包裝結構已經逃避了科學家數十年的研究.
它在在分子水平上擁有一個規則結構的第一個證據,在30年代中期被提出.
[6] [7]
自那時以來,
許多知名學者,
包括諾貝爾獎獲得主Crick, Pauling, Rich 和Yonath,
和其他人,
包括Brodsky, Berman, and Ramachandran,
集中在膠原單體的構型上.
Several competing models, although correctly dealing with the conformation of
each individual peptide chain, gave way to the triple-helical "Madras" model of
Ramachandran, which provided an essentially correct model of the molecule's quaternary
structure[8][9][10] although this model still required
some refinement. [clarification
needed] [11][12][13][14]
The packing structure of collagen has not been defined to the same degree
outside of the fibrillar collagen types, although it has been
long known to be hexagonal or quasi-hexagonal.[15][16][17]
幾個競爭模型,
雖然正確地處理了個別肽鏈的構型,
給予Ramachandran的三螺旋“Madras”的模型方向,
它提供了該分子的四級結構基本上正確的模型[8]
[9] [10],
雖然這種模式仍需要某種程度的完善. [澄清需要]
[11] [12] [13] [14]
膠原的包裝結構尚未被定義為纖維狀膠原類型的相同程度之外,
雖然它長期已已被知道是六邊形或準六邊形.
[15] [16] [17]
As with its monomeric structure, several conflicting models alleged that either
the packing arrangement of collagen molecules is 'sheet-like' or microfibrillar.[18][19]
The microfibrillar structure of collagen fibrils in tendon, cornea and
cartilage has been directly imaged by electron microscopy.[20][21][22]
The microfibrillar structure of tail tendon, as described by Fraser,
Miller, and Wess (amongst others), was modeled as being closest to the observed
structure, although it oversimplified the topological progression of neighboring
collagen molecules, and hence did not predict the correct conformation of the
discontinuous D-periodic pentameric arrangement termed simply: the microfibril.[23][24]
Various cross linking agents like L-Dopaquinone, embeline, potassium embelate
and 5-O-methyl embelin could be developed as potential
cross-linking/stabilization agents of collagen preparation and its application
as wound dressing sheet in clinical applications is enhanced.[25]
在它的單體結構方面,
幾個衝突的模型指稱膠原分子的包裝排列是“片狀”或則是微纖絲.
[18] [19]
在肌腱,
角膜和軟骨裏的膠原纖絲的微原纖結構已經直接以電子顯微鏡成像.
[20] [21] [22]
尾腱的微原纖結構,
如由Fraser, Miller,和Wess(主要),
被建模為最接近於所觀察到的結構,
儘管它過於簡化相鄰膠原分子的拓撲(空間)進展,
因此並不能預測被簡稱為:
微纖維的不連續的D-週期性五聚體結構排列的正確構型.
[23] [24]
各種交聯劑如
L-Dopaquinone,
embeline, potassium embelate
和5-O-methyl embelin,
可以發展為膠原製備和其在臨床應用中傷口敷料片增強應用的潛在的交聯/穩定劑. [25]
Chemistry
Collagen is composed of a triple helix, which generally consists of two
identical chains (α1) and an additional chain that differs slightly in its
chemical composition (α2).[26] The amino acid composition of collagen
is atypical for proteins, particularly with respect to its high hydroxyproline content.
化學
膠原是由一個三螺旋組成,
它一般由兩個相同的鏈(α1)和一個在其化學成分略有不同的附加鏈(α2)組成.[26]
膠原蛋白的氨基酸組成是非典型為蛋白質,
特別是在於它的高hydroxyproline(羥脯氨酸)含量.
The most common motifs in the amino acid sequence of collagen are glycine-proline-X
and glycine-X-hydroxyproline, where X is any amino acid other than glycine,
proline or hydroxyproline. The average amino acid composition for fish and
mammal skin is given.[26]
膠原蛋白的氨基酸序列最常見的順序是glycine-proline-X和glycine-X-hydroxyproline,
其中X是除了glycine,
proline
或
hydroxyproline以外的任何氨基酸.
魚類和哺乳動物皮膚的平均氨基酸組成如下.
[26]
Synthesis
合成
First, a three-dimensional stranded structure is assembled, with the amino acids
glycine and proline as its principal components. This is not yet collagen but
its precursor, procollagen. Procollagen is then modified by the addition of
hydroxyl groups
to the amino acids proline and lysine.
This step is important for later glycosylation and
the formation of the triple helix structure of collagen.
首先,
三維串鏈結構被組裝,
以glycine和proline氨基酸作為其主要部件.
這還不是膠原,
而是其前趨體,
前膠原.
原膠原然後經由加入羥基到proline 和 lysine
氨基酸的修飾.
這個步驟對於後續膠原蛋白的糖基化以及三螺旋結構的形成非常重要.
The hydroxylase enzymes that perform these reactions require Vitamin
C as
a cofactor, and a deficiency in this vitamin results in impaired collagen
synthesis and the resulting disease scurvy[27]
These hydroxylation reactions are catalyzed by two different enzymes:
prolyl-4-hydroxylase[28] and lysyl-hydroxylase.
Vitamin C also serves with them in inducing these reactions. in this service,
one molecule of vitamin C is destroyed for each H replaced by OH. [29]
執行這些反應的羥化酶酶需要維生素C作為輔因子,
並且,
缺乏此維生素導致膠原合成受損以及由此產生的疾病,
壞血病.[27]
這些羥基化反應是由兩種不同的酶催化的:prolyl-4-hydroxylase
[28 ]和lysyl-hydroxylase.
維生素C也提供他們以誘導這些反應.
在這項服務中,
每個H被OH取代時,
子的維生素C會破壞.[29]
The synthesis of collagen occurs inside and outside of the cell. The formation
of collagen which results in fibrillary collagen (most common form) is discussed
here.
Meshwork collagen, which is often involved in the formation of filtration
systems, is the other form of collagen.
All types of collagens are triple helices, and the differences lie in the
make-up of the alpha peptides created in step 2.
膠原蛋白的合成在細胞內部和外面發生.
這裡討論產生纖維膠原(最常見的形式)的膠原蛋白的形成.
網片膠原,
這常常涉及過濾系統的形成,
是另一種形式的膠原蛋白.
所有類型的膠原蛋白都是三螺旋,
而不同之處在於在步驟2中產生的alpha
peptides
的構成.
1.
Transcription of mRNA: About 34 genes are associated
with collagen formation, each coding for a specific mRNA sequence, and typically
have the "COL" prefix. The beginning of collagen synthesis begins with
turning on genes which are associated with the formation of a particular alpha
peptide (typically alpha 1, 2 or 3).
mRNA的轉錄:約34個基因關聯於膠原形成,
每個編碼特定的mRNA序列,
並且通常具有的“COL”字首.
膠原合成的起始是從與特定的alpha peptide(通常為alpha
1, 2或3)的形成相關的基因的開始轉動開始.
2.
Pre-pro-peptide formation: Once the final mRNA exits from the cell nucleus and enters into the cytoplasm, it
links with the ribosomal subunits and the process of translation occurs.
The early/first part of the new peptide is known as the signal sequence. The
signal sequence on the N-terminal of
the peptide is recognized by a signal recognition particle on the endoplasmic
reticulum, which will be responsible for directing the pre-pro-peptide into the
endoplasmic reticulum.
Therefore, once the synthesis of new peptide is finished, it goes directly into
the endoplasmic reticulum for post-translational processing. It is now known as
pre-pro-collagen.
預前肽形成:一旦最終的mRNA從細胞核的出來並進入細胞質,
它與核糖體子單位鏈接而發生轉譯的過程.
新的肽的早期/第一部分被稱為信號序列.
該肽的N-末端的信號序列是由上內質網的信號識別顆粒所識別的,
它將是負責指導前原肽進入內質網.
因此,
一旦新的肽合成完成後,
它會直接進入內質網,
用於轉譯後程序.
它現在被稱為前原膠原.
3.
Alpha peptide to procollagen: Three modifications of the
pre-pro-peptide occur leading to the formation of the alpha peptide. Secondly,
the triple helix known as procollagen is formed before being transported in a
transport vesicle to the Golgi apparatus.
Alpha peptide
到前膠原:三個前原肽的修飾的發生導致的alpha peptide的形成.
其次,
稱為原膠原的三螺旋在被往高爾基體的運輸囊泡運送之前形成.
1) The signal peptide on the N-terminal is dissolved, and the molecule is now
known as propeptide (not procollagen).
N末端上的信號肽被溶解,
此分子現在被稱為前肽(不是前膠原).
2) Hydroxylation of lysines and prolines on propeptide by the enzymes 'prolyl
hydroxylase' and 'lysyl hydroxylase' (to produce hydroxyproline and
hydroxylysine) occurs to aid cross-linking of the alpha peptides. This enzymatic
step requires vitamin C as a cofactor. In scurvy, the lack of hydroxylation of
prolines and lysines causes a looser triple helix (which is formed by three
alpha peptides).
經由
'prolyl hydroxylase' and 'lysyl
hydroxylase'酶(用以產生hydroxyproline and
hydroxylysine)
羥化前肽上的lysines
和prolines
發生了,
以幫助alpha peptides的交聯.
此酶促步驟需要維生素C作為輔因子.
在壞血病,
缺乏prolines
和 lysines的羥基化導致較鬆散的三股螺旋(它是由三個alpha peptides形成的).
3) Glycosylation occurs by adding either glucose or galactose monomers onto the
hydroxy groups that were placed onto lysines, but not on prolines.
糖基化的發生,
是經由加入葡萄糖或半乳糖單體到被放置到lysines而非prolines的羥基基團.
From here the hydroxylated and glycosylated propeptide twists towards the left
very tightly and then three propeptides will form a triple helix.
It is important to remember that this molecule, now known as 'procollagen' (not
propeptide) is composed of a twisted portion (center) and two loose ends on
either end.
At this point, the procollagen is packaged into a transfer vesicle destined for
the Golgi apparatus.
從這裡,
羥基化和糖化的前肽向左非常緊密地曲折,
然後3前肽將形成一個三螺旋.
重要的是要記住,
這個分子,
現在被稱為“前膠原”(不是前肽)是由扭曲的部分(中心)和兩端的兩個鬆的尾端.
這時後,
原膠原被打包到目的地為高爾基體的轉移泡囊.
4.
Golgi apparatus modification: In the Golgi apparatus, the
procollagen goes through one last post-translational modification before being
secreted out of the cell. In this step, oligosaccharides (not monosaccharides as
in step 3) are added, and then the procollagen is packaged into a secretory
vesicle destined for the extracellular space.
高爾基體修飾:在高爾基體,
前膠原在被分泌出細胞前,
經過最後一個轉譯後修飾.
在這個步驟中,
寡糖(不是如在步驟3的單糖)被加入,
然後前膠原被打包到往細胞外空間的分泌囊泡.
5.
Formation of tropocollagen: Once outside the cell, membrane bound enzymes known as 'collagen peptidases', remove
the "loose ends" of the procollagen molecule. What is left is known as
tropocollagen. Defects in this step produce one of the many collagenopathies
known as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. This step is absent when
synthesizing type III, a type of fibrilar collagen.
原膠原蛋白的形成:一旦到細胞外,
被稱為“膠原蛋白肽酶”
的膜結合的酶,
移除了原膠原分子的“鬆的尾端”.
而剩下的被稱為原膠原蛋白.
在這個步驟中的缺陷會產生稱為Ehlers-Danlos徵候群的許多collagenopathies的症狀之一.
當合成III型,
纖維膠原的一型時,
這個步驟不存在.
6.
Formation of the collagen fibril: 'Lysyl oxidase', an
extracellular enzyme, produces the final step in the collagen synthesis pathway.
This enzyme acts on lysines and hydroxylysines producing aldehyde groups, which
will eventually undergo covalent bonding between tropocollagen molecules. This
polymer of tropocollogen is known as a collagen fibril.
膠原纖絲的形成:”Lysyl oxidase
“,
一種胞外酶,
產生在膠原蛋白的合成途徑中的最後步驟.
這種酶作用於lysines和hydroxylysines,
產生醛基,
這最終將經過原膠原分子之間的共價鍵合.
這種原膠原蛋白(tropocollogen)的聚合物被稱為膠纖絲.
Amino acids
氨基酸
Collagen has an unusual amino acid composition and sequence:
膠原具有不尋常的氨基酸組成和序列:
·
Glycine is found at almost every third residue.
Glycine幾乎每三殘基就會發現一個..
·
Proline makes up about 17% of collagen.
Proline大約佔膠原蛋白的17%..
·
Collagen contains two uncommon derivative amino acids not directly
inserted during translation. These amino acids are found at specific locations
relative to glycine and are modified post-translationally by different enzymes,
both of which require vitamin C as
a cofactor.
膠原蛋白含有兩種轉譯過程中沒有直接插入的不常見的衍生氨基酸.
這些氨基酸被發現在相對於glycine的特定位置,
並且通過不同酶的轉譯後修飾,
這兩者(兩種衍生氨基酸)都需要維生素C作為輔因子.
·
Hydroxyproline derived from proline.
從proline衍生的Hydroxyproline.
·
Hydroxylysine derived from lysine - depending on the type of
collagen, varying numbers of hydroxylysines are glycosylated (mostly
having
disaccharides attached).
從lysine衍生的Hydroxylysine
-取決於膠原的類型,
不同的數目的hydroxylysines被糖基化(大多是附著雙醣類).
Cortisol stimulates degradation of
(skin) collagen into amino acids.[30]
皮質醇的刺激(皮膚)膠原降解成氨基酸. [30]
Collagen I formation膠原的形成
Most collagen forms in a similar manner, but the following process is typical
for type I:
大部份的膠原以類似的方式形成,
但下面是I型的典型程序:
1.
Inside the cell在細胞內
1.
Two types of alpha chains are formed during translation on ribosomes along the rough
endoplasmic reticulum (RER):
alpha-1 and alpha-2 chains. These peptide chains (known as preprocollagen)
have registration peptides on each end and a signal peptide.
Polypeptide chains are released into the lumen of the RER.
兩種類型的α鏈在核糖體的轉譯過程中,
沿著粗面內質網(RER)
中形成:
α-1和α-2鏈.
這些肽鏈(稱為preprocollagen)
具有在每端的登記肽以及一個信號肽.
多肽鏈被釋放到RER的腔內.
2.
Signal peptides are cleaved inside the RER and the chains are now known as
pro-alpha chains.
信號肽在RER內被裂解,
而鏈現在被稱為
前-α鏈.
3.
Hydroxylation of lysine and proline amino
acids occurs inside the lumen. This process is dependent on
ascorbic acid (vitamin C) as a cofactor.
lysine 和 proline 氨基酸的羥化在腔內發生.
這個過程依賴維生素C作為輔因子.
4.
Glycosylation of specific hydroxylysine residues
occurs.特定hydroxylysine殘基糖基化的發生.
5.
Triple alpha helical structure is formed inside the endoplasmic reticulum from
two alpha-1 chains and one alpha-2 chain.
三重α螺旋結構由兩個α-1鏈和1α-2鏈在內質網內形成.
6.
Procollagen is shipped to the Golgi apparatus, where it is packaged and
secreted by exocytosis.
前膠原被運到高爾基體,
在那裡它被打包並經由胞吐分泌.
2.
Outside the cell細胞外
1.
Registration peptides are cleaved and tropocollagen is formed by procollagen
peptidase.
經由“膠原蛋白肽酶”,
註冊肽被裂解形成了原膠原蛋白.
2.
Multiple tropocollagen molecules form collagen fibrils, via covalent
cross-linking (aldol reaction)
by lysyl oxidase which links hydroxylysine and lysine
residues.
Multiple collagen fibrils form into collagen fibers.
經由lysyl oxidase
鏈接hydroxylysine和lysine殘基的共價交聯(aldol反應),
多個原膠原蛋白分子形成膠原纖絲.
多個膠原纖絲形成為膠纖絲.
3.
Collagen may be attached to cell membranes via several types of protein,
including fibronectin and
integrin.
膠原可以經由多種類型的蛋白質,
包括fibronectin 和integrin,
附著到細胞膜.
Synthetic pathogenesis合成相關的發病機理
Vitamin C deficiency causes scurvy, a serious and painful disease in which defective collagen prevents
the formation of strong connective tissue. Gums deteriorate
and bleed, with loss of teeth; skin discolors, and wounds do
not heal. Prior to the 18th century, this condition was notorious among
long-duration military, particularly naval, expeditions during which
participants were deprived of foods containing vitamin C.
維生素C缺乏會導致壞血病,
是一種嚴重和痛苦的疾病,
其中有缺陷的膠原蛋白阻止了強固的結締組織的形成.
牙齦惡化和流血,
缺掉牙;
皮膚褪色,
和傷口不癒合.
在18世紀之前,
這種情況在長期軍隊徵戰期間,
人員被剝奪了含維生素C的食物,
尤其是海軍,
是臭名昭著的.
An autoimmune disease such as lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid
arthritis[31] may attack healthy collagen fibers.
Many bacteria and viruses secrete virulence factors, such as the enzyme collagenase, which destroys collagen or
interferes with its production.
一種自體免疫性疾病,
如系統性紅斑狼瘡或類風濕性關節炎[31]可能攻擊健康的膠纖絲.
許多細菌和病毒分泌的毒力因子,
如膠原酶,
它破壞膠原或干擾其生產.
Molecular structure分子結構
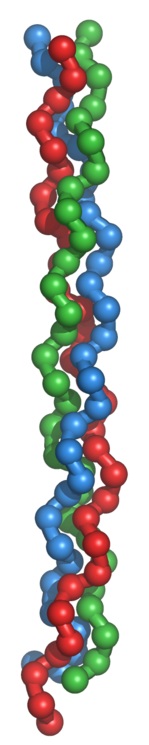
A single collagen molecule (also known as tropocollagen) is used to make up
larger collagen aggregates, such as fibrils. It is approximately 300 nm long
and 1.5 nm in diameter, and it is made up of three polypeptide strands
(called alpha peptides, see step 2), each of which has the conformation of a
left-handed helix –
this should not be confused with the right-handed alpha
helix.
These three left-handed helices are twisted together into a right-handed triple
helix or "super helix", a cooperative quaternary
structure stabilized
by many hydrogen
bonds.
With type I collagen and possibly all fibrillar collagens, if not all collagens,
each triple-helix associates into a right-handed super-super-coil referred to as
the collagen microfibril.
Each microfibril is interdigitated with
its neighboring microfibrils to a degree that might suggest they are
individually unstable, although within collagen fibrils, they are so well
ordered as to be crystalline.
單一的膠原分子(也稱為原膠原)被用來組成較大的膠原聚集體,
如纖維.
它約大約是300納米長,
直徑1.5納米,
它是由三條多肽鏈(稱為alpha
peptides,
見步驟2),
每一個都具有一個左手螺旋的構型
-
這不應該與右旋α螺旋混淆.
這三個左旋螺旋絞合在一起成為右旋三螺旋或“超級螺旋”,
是由許多氫鍵穩定化的一個合作的四級結構.
以I型膠原蛋白,可能所有纖維狀膠原,
即使不是全部的膠原,
每三螺旋聯結成稱為膠原纖絲的右旋超-超級線圈.
每個纖絲與其相鄰的纖絲相互交叉到達一定程度,
可能暗示它們是單獨不穩定的,
雖然膠原纖絲內,
它們是被如此良好地被結晶排序的.
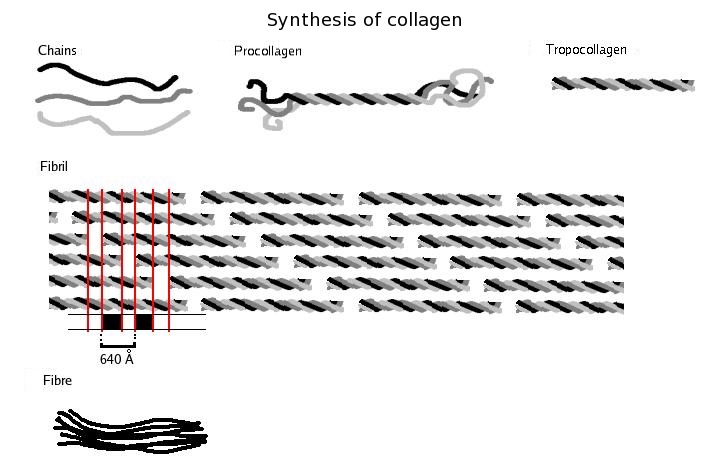
Three polypeptides coil
to form tropocollagen. Many tropocollagens then bind together to form a fibril,
and many of these then form a fibre.
三個多肽線圈形成原膠原蛋白.
許多原膠原蛋白然後結合在一起以形成纖絲,
並且許多這些然後形成纖維.
Distinctive feature of collagen
is the regular arrangement of amino acids in
each of the three chains of these collagen subunits. The sequence often follows
the pattern Gly-Pro-X
or Gly-X-Hyp, where X may be any of various other amino acid residues.[26]
Proline or hydroxyproline constitute about 1/6 of the total sequence. With
glycine accounting for the 1/3 of the sequence, this means approximately half of
the collagen sequence is not glycine, proline or hydroxyproline, a fact often
missed due to the distraction of the unusual GX1X2 character
of collagen alpha-peptides.
膠原蛋白的顯著特點是這些膠原次單位的每個三條鏈中的氨基酸的規則排列.
其序列經常遵循
Gly-Pro-X
或 Gly-X-Hyp的型式,
其中X可以是任何其他不同的氨基酸殘基. [26]
Proline或hydroxyproline,
約佔所有序列的1/6. glycine佔有這些序列的1/3,
這意味著大約有一半的膠原序列的不是glycine, proline
或 hydroxyproline,
一個由於膠原α-肽的不尋常GX1X2性質的攪動而經常錯過的事實
The high glycine content of collagen is important with respect to stabilization
of the collagen helix as this allows the very close association of the collagen
fibers within the molecule, facilitating hydrogen bonding and the formation of
intermolecular cross-links.[26]
This kind of regular repetition and high glycine content is found in only a few
other fibrous proteins, such as silk fibroin.
About 75–80% of silk is (approximately) -Gly-Ala-Gly-Ala- with 10% serine, and elastin is
rich in glycine, proline, and alanine (Ala), whose side group is
a small methyl group.
Such high glycine and regular repetitions are never found in globular proteins
save for very short sections of their sequence.
膠原蛋白的高的glycine含量對於膠原螺旋的穩定化是很重要的,
因為這可以使分子內的膠原纖微非常密切的聯結,
使容易形成氫鍵和分子間的交聯. [26]
這種規則的重複和高glycine的含量只有在幾個其他纖維狀蛋白質被發現,
例如絲纖蛋
約75-80%的絲是(大約) -Gly-Ala-Gly-Ala-
有10%serine,
而elastin 富含glycine, proline,
和 alanine (Ala),
其側基是一個小甲基.
如此高的glycine和規則重複是從不曾在球狀蛋白質發現的,
使它們的序列截面非常地短.
Chemically reactive side groups are not needed in structural
proteins, as they are in enzymes and transport proteins; however, collagen is not quite just a
structural protein. Due to its key role in the determination of cell phenotype,
cell adhesion, tissue regulation and infrastructure, many sections of its
non-proline-rich regions have cell or matrix association / regulation roles.
結構蛋白質不需要像酶和轉輸蛋白一樣需要有化學反應性的側基團,
然而,
膠原蛋白是不太只是一個結構蛋白.
由於它在細胞表型,
細胞粘附,
組織調控和基礎構成等具有關鍵的作用,
其非富含proline區域的許多區段具有細胞或基質聯結/調節的角色.
The relatively high content of proline and hydroxyproline rings, with their
geometrically constrained carboxyl and (secondary) amino groups, along with the rich abundance
of glycine, accounts for the tendency of the individual polypeptide strands to
form left-handed helices spontaneously, without any intrachain hydrogen bonding.
相對高含量的proline和hydroxyproline環,
以其被幾何約束的羧基和(二度)氨基,
伴隨著富豐的glycine,
佔有了個體多肽鏈自發形成左旋螺旋的傾向,
而沒有任何鏈內氫鍵.
Because glycine is the smallest
amino acid with no side chain, it plays a unique role in fibrous structural
proteins.
In collagen, Gly is required at every third position because the assembly of the
triple helix puts this residue at the interior (axis) of the helix, where there
is no space for a larger side group than glycine’s single hydrogen atom.
For the same reason, the rings of the Pro and Hyp must point outward.
These two amino acids help stabilize the triple helix—Hyp even more so than Pro;
a lower concentration of them is required in animals such as fish, whose body
temperatures are lower than most warm-blooded animals.
因為glycine是最小的氨基酸,
沒有側鏈,
它在纖維結構蛋白具有獨特的角色.
在膠原蛋白裏,在每一個第三位置需要Gly,
因為三重螺旋的組合把這個殘基放
在螺旋內部(軸), 那裡沒有給比glycine的單個氫原子更大的側基的空間.
出於同樣的原因,
Pro
和 Hyp的環必須朝外.
這兩種氨基酸有助於穩定三股螺旋---Hyp甚至比Pro更`是如此;
在例如魚的動物,
它們需要較低的濃度,
其體溫比大多數溫血動物低.
Lower proline and hydroxyproline contents are characteristic of cold-water, but
not warm-water fish; the latter tend to have similar proline and hydroxyproline
contents to mammals.[26] The
lower proline and hydroxproline contents of cold-water fish and other poikilotherm animals
leads to their collagen having a lower thermal stability than mammalian
collagen.[26] This
lower thermal stability means that gelatin derived
from fish collagen is not suitable for many food and industrial applications.
較低的proline
和 hydroxyproline含量是冷水,
而不是溫水魚的特性;
後者傾向於具有相似於哺乳動物的proline
和 hydroxyproline的含量. [26]
冷水魚及其他的冷血動物導致其膠原蛋白具有較低的熱穩定. [26]
此較低的熱穩定意味著從魚膠原衍生的明膠不適合許多食品和工業應用.
The tropocollagen subunits spontaneously self-assemble, with regularly staggered ends, into even
larger arrays in the
extracellular spaces of tissues.[32][33]
In the fibrillar collagens, the molecules are staggered from each other by about
67 nm (a
unit that is referred to as ‘D’ and changes depending upon the hydration state
of the aggregate).
原膠原次單位的自發地自組裝,
以規則的交錯的末端,
在細胞外空間,
成為甚至更大的陣列. [32][33]
在纖維狀膠原,
分子彼此互相以大約67納米(一個稱為”D”的單位,
且取決於聚集體的水合狀態而變化)交錯.
Each D-period contains four plus a fraction collagen molecules, because 300 nm
divided by 67 nm does not give an integer (the length of the collagen molecule
divided by the stagger distance D).
Therefore, in each D-period repeat of the microfibril, there is a part
containing five molecules in cross-section, called the “overlap”, and a part
containing only four molecules, called the "gap".[23]
The triple-helices are also arranged in a hexagonal or quasi-hexagonal array in
cross-section, in both the gap and overlap regions.[15][23]
每個D-週期包含四個加一個分數的膠原分子,
因為300nm被67納米不能整除(膠原分子的長度除以交錯距離D).
因此,
在纖絲的每一個D週期重複,
有一個部份在橫截面含有5的分子,
被稱為“重疊”,
而有一個部份只含有4的分子,
被稱為 ”間隙”. [23]
三重螺旋在橫截面也排列成六邊形或準六邊形陣列,
在重疊及間隙這兩個區域都是. [15][23]
There is some covalent crosslinking within the triple helices, and a variable
amount of covalent crosslinking between tropocollagen helices forming well
organized aggregates (such as fibrils).[34]
Larger fibrillar bundles are formed with the aid of several different classes of
proteins (including different collagen types), glycoproteins and proteoglycans
to form the different types of mature tissues from alternate combinations of the
same key players.[33]
在三螺旋中有一些共價的交聯,
以及原膠原蛋白螺旋之間一個可變數量的共價交聯,
形成組織良好的聚集物(如纖絲). [34]
更大的纖維束是有幾個不同的類蛋白(包括不同膠原蛋白的類型),
糖蛋白和蛋白多醣的幫助而形成,
以從相同的關鍵成員的交替組合形成不同型態的成熟組織. [33]
Collagen's insolubility was
a barrier to the study of monomeric collagen until it was found that
tropocollagen from young animals can be extracted because it is not yet fully crosslinked.
However, advances in microscopy techniques (i.e. electron microscopy (EM) and
atomic force microscopy (AFM)) and X-ray diffraction have enabled researchers to
obtain increasingly detailed images of collagen structure in situ.
膠原的不溶性是單體膠原蛋白研究的一個障礙,
直到發現從年輕動物的原膠原可以被提取,
因為它尚未完全交聯.
但是,
在顯微技術的進步(如電子顯微鏡(M)原子力顯微鏡(FM)),
以及X射線繞射已經使研究人員能就地得到越來越詳細的膠原結構圖像.
These later advances are particularly important to better understanding the way
in which collagen structure affects cell–cell and cell–matrix communication, and
how tissues are constructed in growth and repair, and changed in development and
disease.[35][36]
For example using AFM–based nanoindentation it has been shown that a single
collagen fibril is a heterogeneous material along its axial direction with
significantly different mechanical properties in its gap and overlap regions,
correlating with its different molecular organizations in these two regions.[37]
這些後來的進展是特別重要的,
以更好地理解膠原結構影響
細胞-細胞
和細胞 -
基質的通聯方式,
以及組織在生長和修復中如何被建構,
以及在發育和疾病時如何被改變. [35][36]
例如使用基於AFM的納米壓痕,
它已經顯示出,
單一的膠原纖絲是沿其軸向方向,
在其間隙和重疊的區域有著顯著不同的機械性能,
的異質材料,
與它在這兩個區域的不同分子組織關聯. [37]
Collagen fibrils/aggregates are
arranged in different combinations and concentrations in various tissues to
provide varying tissue properties. In bone, entire collagen triple helices lie
in a parallel, staggered array.
40 nm gaps between the ends of the tropocollagen subunits (approximately equal
to the gap region) probably serve as nucleation sites for the deposition of
long, hard, fine crystals of the mineral component, which is (approximately) Ca10(OH)2(PO4)6.[38]
Type I collagen gives bone its tensile
strength.
膠原纖絲/聚集體在各種組織中被排列成不同的組合和濃度,
以提供不同的組織性質.
在骨,
整個膠原三螺旋位於一個平行,
交錯陣列.
的原膠原次單位(大約等於間隙區域)
的端部之間的40nm的間隙,
可能充當成核位點,
用於礦物成分的長,
硬,
微細結晶的沉積,
這大約是Ca10(OH)2(PO4)6. [38] I型膠原給予骨的抗張強度.
Types and associated disorders
類型和相關疾病
Collagen occurs in many places throughout the body. Over 90% of the collagen in
the body, however, is type I.[39]
So far, 28 types of collagen have been identified and described. The five
most common types are:
膠原蛋白發生在整個身體的許多地方.
然而,
在體內超過90%的膠原蛋白是I型[39]
到目前為止,
28種膠原的已被鑑定和描述.
五個最常見的類型有:
·
Type I: skin, tendon,
vascular ligature, organs, bone (main component of the organic part of bone)
I型:皮膚,
腱,
血管連結,
器官,
骨(骨的有機部分的主要成分)
·
Type II: cartilage (main component of cartilage)
II型:軟骨(軟骨的主要成分)
·
Type III: reticulate (main
component of reticular fibers), commonly found alongside
type I.
III型:網紋(網狀纖維的主要成分),
通常沿著類型I.被發現
·
Type IV: forms basal lamina,
the epithelium-secreted layer of the basement membrane.
IV型:形成基底膜,
基底膜的上皮分泌層.
·
Type V: cell surfaces, hair
and placenta
V型:細胞表面,
頭髮和胎盤
Collagen-related diseases most commonly arise from genetic defects or
nutritional deficiencies that affect the biosynthesis, assembly,
postranslational modification, secretion, or other processes involved in normal
collagen production.
膠原相關疾病最常源起於遺傳缺陷或營養缺乏,
它影響的生化合成,
組構,
轉譯後修飾,
分泌,
或參與正常膠原蛋白產生的其它程序.
|
Genetic Defects of Collagen Genes
膠原蛋白基因的遺傳缺陷
|
|
Type類型
|
Notes
備註
|
Gene(s)
基因
|
Disorders障礙
|
|
I
|
This is the most abundant collagen of the human body. It is present in
scar tissue, the end product when tissue heals by
repair. It is found in tendons, skin, artery
walls, cornea, the
endomysium surrounding muscle fibers,
fibrocartilage, and the organic part of bones and teeth.
這是人體內最豐富的膠原蛋白. 它是呈現在疤痕組織內,
是組織修復癒合時的最終產品.
它被發現在肌鍵,皮膚,動脈壁,
角膜,
圍繞在肌肉纖維的內膜,
纖維軟骨,
以及骨骼和牙齒中的有機部分的.
|
COL1A1,COL1A2
|
Osteogenesis
imperfecta,Ehlers–Danlos
syndrome,Infantile
cortical hyperostosis aka
Caffey's disease
|
|
II
|
Hyaline cartilage,
makes up 50% of all cartilage protein. Vitreous humour of the eye.
透明軟骨, 構成所有軟骨蛋白的50%.
眼睛的玻璃體.
|
COL2A1
|
Collagenopathy, types II and XI
|
|
III
|
This is the collagen of granulation tissue,
and is produced quickly by young fibroblasts before the tougher type I collagen
is synthesized.
Reticular fiber. Also found in artery
walls, skin, intestines and the uterus
這是肉芽組織的膠原蛋白,
並且是在更嚴格的I型膠原蛋白被合成之前,由年輕成纖維細胞迅速地產生.
網狀纖維. 在動脈壁,
皮膚,
腸道,
子宮也發現.
|
COL3A1
|
Ehlers–Danlos
syndrome,Dupuytren's
contracture
|
|
IV
|
Basal lamina; eye lens. Also serves as part of the
filtration system in capillaries and the glomeruli of nephron in
the kidney.
基底層;
眼球晶狀體.
也用作在毛細管和在在腎臟裏的腎單位的腎小球過濾系統的一部份.
|
COL4A1,COL4A2,COL4A3,COL4A4,COL4A5,COL4A6
|
Alport syndrome,Goodpasture's
syndrome
|
|
V
|
Most interstitial tissue, assoc. with type I, associated with placenta
大多數間質組織,
與I型關聯,
與胎盤關聯.
|
COL5A1,COL5A2,COL5A3
|
Ehlers–Danlos
syndrome(Classical)
|
|
VI
|
Most interstitial tissue, assoc. with type I
大多數間質組織,
與I型關聯,
與胎盤關聯.
|
COL6A1,COL6A2,COL6A3,COL6A5
|
Ulrich myopathy, Bethlem myopathy, Atopic dermatitis[40]
|
|
VII
|
Forms anchoring fibrils in dermoepidermal
junctions
構成在真皮交界處的錨原纖維.
|
COL7A1
|
Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica
|
|
VIII
|
Some endothelial cells
一些內皮細胞
|
COL8A1,COL8A2
|
Posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy 2
|
|
IX
|
FACIT collagen, cartilage, assoc. with
type II and XI fibrils.
FACIT膠原,
軟骨,
與I型II型和XI纖絲關聯
FACIT
(Fibril Associated Collagens with Interrupted Triple helices)
|
COL9A1,COL9A2,COL9A3
|
EDM2 and EDM3
|
|
X
|
Hypertrophic and mineralizing cartilage|
肥厚和礦化軟骨
|
COL10A1
|
Schmid
metaphyseal dysplasia
|
|
XI
|
Cartilage
軟骨
|
COL11A1,COL11A2
|
Collagenopathy, types II and XI
|
|
XII
|
FACIT collagen, interacts with type I
containing fibrils, decorin and
glycosaminoglycans.
FACIT膠原蛋白,
與I型交互做用,
含纖維,蛋白多醣和粘多醣
|
COL12A1
|
–
|
|
XIII
|
Transmembrane collagen, interacts with integrin a1b1, fibronectin and components of basement membranes
like nidogen and perlecan.
與integrin a1b1,
纖連蛋白和基底膜的組分如象巢蛋白和串珠素等交互作用.
|
COL13A1
|
–
|
|
XIV
|
FACIT collagen, also known as undulin
FACIT膠原蛋白,
也稱為粗纖維調節素.
|
COL14A1
|
–
|
|
XV
|
–
|
COL15A1
|
–
|
|
XVI
|
–
|
COL16A1
|
–
|
|
XVII
|
Transmembrane collagen, also known as BP180, a 180 kDa protein
跨膜膠原, 也稱為BP180, 180 kDa
分子量的蛋白.
|
COL17A1
|
Bullous pemphigoid and certain forms of junctionalepidermolysis
bullosa
|
|
XVIII
|
Source of endostatin
血管內皮抑制素的來源.
|
COL18A1
|
–
|
|
XIX
|
FACIT collagen
FACIT膠原蛋白
|
COL19A1
|
–
|
|
XX
|
–
|
COL20A1
|
–
|
|
XXI
|
FACIT collagen
|
COL21A1
|
–
|
|
XXII
|
–
|
COL22A1
|
–
|
|
XXIII
|
MACIT collagen
|
COL23A1
|
–
|
|
XXIV
|
–
|
COL24A1
|
–
|
|
XXV
|
–
|
COL25A1
|
–
|
|
XXVI
|
–
|
EMID2
|
–
|
|
XXVII
|
–
|
COL27A1
|
–
|
|
XXVIII
|
–
|
COL28A1
|
–
|
In addition to the above-mentioned disorders, excessive deposition of collagen
occurs in scleroderma.
除了上面提到的病症,
膠原的過度沉積發生在硬皮病.
Diseases
疾病
One thousand mutations have been identified in twelve out of more than twenty
types of collagen. These mutations can lead to various diseases at the tissue
level.[41]
一千種的突變已經從多於二十多個類型的膠原蛋白的12個中被確定出來.
這些突變可以導致在組織層次的各種疾病.
[41]
Osteogenesis imperfecta – Caused by a mutation in type 1 collagen, dominant
autosomal disorder, results in weak bones and irregular connective tissue, some
cases can be mild while others can be lethal, mild cases have lowered levels of
collagen type 1 while severe cases have structural defects in collagen.[42]
成骨不全症
-
由1型膠原蛋白的突變引起的,
主導常染色體的疾病,
導致骨骼脆弱和不規則的結締組織,
部分病例可能是輕度的,
而另一些可能是致命的.
溫和的情況有低水平的I型膠原蛋白,
而嚴重情況具有在膠原結構上的缺陷. [42]
Chondrodysplasias – Skeletal disorder believed to be
caused by a mutation in type 2
collagen, further research is being conducted to confirm this.[43]
軟骨發育異常
-
骨骼病症,
相信是由2型膠原中的突變引起的,
進一步的研究正在進行以確認此問題[43].
Ehlers-Danlos
Syndrome – Six different
types of this disorder, which lead to deformities in connective tissue. Some
types can be lethal, leading to the rupture of arteries. Each syndrome is caused
by a different mutation, for example type four of this disorder is caused by a
mutation in collagen type 3.[44]
Ehlers-Danlos -
徵候群 -
六種不同類型的這種疾病,
它導致結締組織畸形.
一些類型可以是致命的,
導致動脈的破裂.
每個症候群是由一個不同的突變引起的,
對於這種疾病的實例類型4是由在膠原類型3的突變引起的. [44]
Alport syndrome – Can be passed on genetically,
usually as X-linked dominant, but also as both an autosomal dominant and
autosomal recessive disorder, sufferers have problems with their kidneys and
eyes, loss of hearing can also develop in during the childhood or adolescent
years.[45]
Alport徵候群 -
可在基因上傳遞,
通常為X連鎖顯性,
也既是常染色體顯性遺傳和常染色體隱性遺傳疾病,
患者有他們的腎臟和眼睛的問題,
聽力損失也會在兒童期或青春期發展.
[45]
Osteoporosis – Not inherited genetically, brought
on with age, associated with reduced levels of collagen in the skin and bones,
growth hormone injections are being researched as a possible treatment to
counteract any loss of collagen.[46]
骨質疏鬆症
–
一般不會基因遺傳,
隨著年齡的增長帶來的,
與膠原在皮膚和骨頭的水平降低相關,
正在研究注射生長激素作為一種可能的治療,
以抵制膠原的任何損失[46].
Knobloch syndrome – Caused by a mutation in the collagen XVIII gene, patients
present with protrusion of the brain tissue and degeneration of the retina, an
individual who has family members suffering from the disorder are at an
increased risk of developing it themselves as there is a hereditary link.[41]
Knobloch syndrome
–
由在膠原XVIII基因中的突變引起的,
患者呈現腦組織的突起和視網膜的變性,
具有為這種疾並病所苦的家庭成員的個個體之,
是有增加其自身發展的風險,
因為這裡有遺傳性的關聯.
[41]
Characteristics特點
Collagen is one of the long, fibrous structural proteins whose functions are quite different
from those of globular proteins, such as enzymes.
Tough bundles of collagen called collagen
fibers are a major component of
the extracellular
matrix that supports most
tissues and gives cells structure from the outside, but collagen is also found
inside certain cells.
Collagen has great tensile strength, and is the main component
of fascia, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, bone and
skin.[47][48] Along with soft keratin, it is responsible for skin strength
and elasticity, and its degradation leads to wrinkles that accompany
aging.[49][50] It strengthens blood vessels and plays a role in tissue development.
It is present in the cornea and lens of the eye in crystalline form.
膠原蛋白是長纖維狀結構蛋白質,
其功能與那些球狀蛋白,
例如酶,
是相當不同的.
稱為膠原纖維的強韌束狀的膠原是支持大部份組織和從外部給予細胞結構的細胞外基質的主要成分,
但膠原也在某些細胞內發現.
膠原具有很大的拉伸強度,
並且是筋膜,
軟骨,
韌帶,
腱,
骨和皮膚的主要成分. [47][48]
隨著軟角蛋白,
它是主管皮膚的強度和彈性,
以及其退化,
導致伴隨老化的皺紋. [49][50]
它加強化血管和參與組織發育的角色.
它以結晶型態存在於眼睛的角膜和晶狀體.
Uses用途
Collagen has a wide variety of applications, from food to medical. For instance,
it is used in cosmetic surgery and burns surgery. It is widely used in the
form of collagen casings for
sausages, which are also used in the manufacture of musical strings.
膠原具有廣泛的應用,
從食物到醫療.
例如,
它是用在美容外科及燒傷手術.
它以廣泛地以膠原腸衣香腸的形式被應用,
它也可用於樂器弦的製造.
If collagen is subject to sufficient denaturation, e.g. by heating, the three
tropocollagen strands separate partially or completely into globular domains,
containing a different secondary structure to the normal collagen polyproline II
(PPII), e.g. random coils. This process describes the
formation of gelatin, which is used in many foods, including flavored gelatin desserts.
Besides food, gelatin has been used in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and photography
industries.[51]
如果膠原蛋白受到足夠的變性,
如通過加熱,
三個原膠原練部分或完全分開成球狀結構域,
含有正常的polyproline II (PPII)膠原不同的二級結構,
例如隨機線圈.
這個過程描述了明膠的型成,
這用在許多食品中,
包括調味明膠甜點的.
除了食品,
明膠已用於製藥,
化妝品,
和攝影行業. [51]
From a nutritional point of view, collagen and gelatin are a poor-quality sole
source of protein since they do not contain all the
essential amino
acids in the proportions
that the human body requires—they are not 'complete proteins' (as defined by food
science, not that they are partially structured).
Manufacturers of collagen-based dietary supplements claim that their products can improve
skin and fingernail quality as well as joint health.
However, mainstream scientific research has not shown strong evidence to support
these claims.[citation
needed] Individuals
with problems in these areas are more likely to be suffering from some other
underlying condition (such as normal aging, dry skin, arthritis etc.) rather
than just a protein deficiency.
從營養角度來看,
膠原蛋白和明膠是較差的單一蛋白質來源,
因為它們不包含
人的身體所需要比例的全部必要氨基酸--他們不是 ”完全蛋白質”
(由食品科學界定,
而不是他們的部分結構化).
膠原蛋白為基礎的膳食補充劑生產商聲稱他們的產品可以改善皮膚和指甲的質量和關節的健康.
然而,
主流的科學研究沒有顯示出強有力的證據來支持這些說法.
[編輯]
在這些方面有問題的人,
更容易受苦於來自於其他一些基本的條件(如正常的老化,
皮膚乾燥,
關節炎等)而不僅僅是一種蛋白質缺乏.
From the Greek for glue, kolla,
the word collagen means "glue producer" and refers to the early
process of boiling the skin and sinews of horses and
other animals to obtain glue. Collagen adhesive was used by Egyptians about 4,000 years ago, and Native
Americans used it in bows about
1,500 years ago.
The oldest glue in the world, carbon-dated as more than 8,000 years old, was
found to be collagen—used as a protective lining on rope baskets and embroidered fabrics, and to hold utensils together; also in crisscross
decorations on human skulls.[52]
來自希臘的膠水,
kolla,
膠原這個字的意思是“膠水生產者”,
指的是早期煮沸馬和其它動物的皮膚和筋以獲得膠的過程.膠原蛋白膠粘劑大約在4000年前被埃及人所使用,
而美洲原住民約在1500年前,
將用它在弓上.
在世界上最古老的膠水,
(同為素)碳日期為8000多年之久,
被認為是膠原蛋白--用作繩索籃子保護內襯,
和繡花面料,
以及維持用具在一起;
也用在人類頭骨上縱橫交錯的裝飾品.
[52]
Collagen normally converts to gelatin, but survived due to dry conditions.
Animal glues are thermoplastic, softening again upon
reheating, and so they are still used in making musical instruments such as fine violins and guitars, which may have to be reopened for repairs—an application
incompatible with tough, synthetic plastic adhesives,
which are permanent. Animal sinews and skins, including
leather, have been used to make useful
articles for millennia.
Gelatin-resorcinol-formaldehyde glue (and with formaldehyde replaced
by less-toxic pentanedial and ethanedial) has been used to repair
experimental incisions in rabbit lungs.[53]
膠原蛋白通常轉化為明膠,
但由於乾燥條件下能倖存.
動物膠是熱塑性的,
在再加熱後再軟化,
因此它們仍然用於製作樂器,
如精製的提琴和吉他,
這些可能要被重新打開進行修理
---
是一個與具有堅韌,
合成塑料的永久的粘合劑,
是不相容的應用.
動物的筋皮及膚皮,
包括皮革,已經被用來製作有用的物品˙幾千年了.
明膠
-
間苯二酚 -
甲醛膠(和以毒性較低的pentanedial
和 ethanedial取代formaldehyde)已被用於修復在兔肺部的實驗切口. [53]
Medical uses醫療用途
Cardiac applications
心臟應用
The four collagenous valve rings,
the central body of the heart and the
extended cardiac skeleton of the heart are histologically and
uniquely bound to cardiac muscle.
Collagen is the floor of the atria adjoining the ceiling of the ventricles.
Collagen contribution to cardiac performance summarily represents an essential,
unique and moving solid form of mass opposed to the fluid mechanics of blood mass
movement within the heart.
The collagenous structure that divides the upper chambers of the heart from the
lower chambers is an impermeable firewall that excludes both blood and
electrical influence through customary anatomical channels.
四個膠原的閥環,
心臟的中央主體和心臟的延伸的心臟骨架,
組織學和獨特地連結到心肌.
膠原蛋白是心房的底層毗鄰心室的頂層.
膠原蛋白對於心臟功能的貢獻摘要地代表了一個必要的,
獨特,
以及質量的動態固體形態,
對應於心臟內血液的流體力學的質量移動.
劃分心臟的上腔與下腔的膠原結構的膠原蛋白,
是一個不滲漏的防火牆,
它排除通過慣常的的解剖途徑的電流和血液的影響.
Thanks to collagen, atrial fibrillation almost never deteriorates to
ventricular
fibrillation. Collagen is infiltrated in varying densities with
cardiac muscle mass. The amount (mass), distribution, age and density of
collagen all contribute to the compliance required to move blood back and forth.
Individual cardiac valvular leaflets are forged into shape by specialized
collagen under variable pressure.
多虧了膠原蛋白,
房顫幾乎從來沒有惡化到室顫.
膠原蛋白以各種不同密度是滲透於心臟的肌肉質量.
其量(質量),
分佈,
年齡和膠原蛋白的密度都有助於來回移動血液的要求的符合性.
個別心臟瓣膜的小葉是由特別化的膠原在可變的壓力下鍛造成形的.
Gradual calcium deposition within collagen occurs
as a natural consequence of aging. Calcium rich fixed points within collagen in
a moving display of blood and muscle enables methods of cardiac imaging technology to arrive at ratios
essentially stating blood in (cardiac input) and blood out (cardiac output). Pathology of the collagen
underpinning of the heart is closely related to the category connective
tissue disease.
在膠原內逐漸的鈣沉積的發生是老化的自然結果.
在一個血液和肌肉的運動顯示下的膠原蛋白內鈣豐富的固定點,
使能做到心臟成像技術的方法,
以得到血液進入(心臟輸入)和血液流出(心輸出量)比例的必要說明.
心臟的膠原蛋白基底的病理是密切與結締組織病的類別相關.
Type II collagen and rheumatoid arthritis
According to a study[54] published in the journal Science, oral
administration of type II collagen improves symptoms of
rheumatoid
arthritis. The authors conducted a randomized, double-blind trial
involving 60 patients with severe, active rheumatoid arthritis.
A decrease in the number of swollen joints and tender joints occurred in
subjects fed with chicken type II collagen for 3 months, but not in those that
received a placebo. Four patients in the collagen group had complete remission
of the disease. No side effects were evident.
II型膠原蛋白和類風濕關節炎
根據一項發表在Science雜誌上的研究[54],
口服II型膠原蛋白改類風濕關節炎善的症狀.
作者進行了涉及60個有嚴重,
活性類風濕關節炎的患者的隨機,
雙盲試驗.
一個在關節腫脹和觸痛關節數量的減少,
發生在投餵以
雞II型膠原3個月的受試者,
而不是在那些接受安慰劑的.
在膠原蛋白組的四名病人有疾病的完全緩解.
無明顯的副作用.
Hydrolyzed type II collagen and osteoarthritis
水解II型膠原和骨關節炎
A published study[55] reports that ingestion of a novel low
molecular weight hydrolyzed chicken sternal cartilage extract, containing a
matrix of hydrolyzed type II collagen, chondroitin sulfate,
and hyaluronic acid, marketed under the brand
name BioCell
Collagen, relieves joint discomfort associated with osteoarthritis.
A randomized
controlled trial (RCT)
enrolling 80 subjects demonstrated that BioCell Collagen was well tolerated with
no serious adverse event and led to a significant improvement
in joint mobility compared to the placebo group on days 35 (p = 0.007) and 70 (p
< 0.001).
已發布的研究[55]報告說,
攝取了一種新的低分子量的水解雞胸骨軟骨提取物,
含有水解的II型膠原,
硫酸軟骨素和透明質酸,
在BioCell
Collagen的品牌名稱下,
的一種基質,
解除了與骨關節炎相關聯的關節不適.
一項招收了80位受試者的隨機對照試驗(RCT),
證明了BioCell膠原良好的耐受性,
無嚴重不良副作用,
並獲致在第35日(P
= 0.007)和第70日(P
<0.001)與安慰劑組相比的關節活動的一個顯著的改善,.
Cosmetic surgery 整容
Collagen has been widely used in cosmetic surgery, as a healing aid for burn
patients for reconstruction of bone and a wide variety of dental, orthopedic,
and surgical purposes. Both human and bovine collagen is widely used as dermal
fillers for treatment of wrinkles and skin aging.[50] Some
points of interest are:
膠原已被廣泛用於整容手術,
作為燒傷患者重建骨和各種各樣的牙齒,
整形外科,
和外科目的一個癒合助劑.
人類和牛膠原蛋白兩者都被廣泛用作皮膚填充劑,
用於治療皺紋和皮膚老化[50]一些關注的要點是:
-
when used cosmetically, there is a
chance of allergic reactions causing prolonged redness; however, this can be
virtually eliminated by simple and inconspicuous patch testing prior to cosmetic use, and
作為化妝使用時,
有造成長期的發紅的過敏反應的機會;
不過這可在美容使用之前,
以簡單和不顯眼的貼片測試來排除,
並且
-
most medical collagen is derived
from young beef cattle (bovine) from certified BSE-free
animals. Most manufacturers use donor animals from either "closed herds", or
from countries which have never had a reported case of BSE such as Australia,
Brazil, and New Zealand.
大多數醫療膠原蛋白是從
認證無狂牛病動物的年輕肉牛(牛)產生的.
大多數製造商使用從
”封閉牛群”,
或從從未有過BSE病例報告的國家,
如澳大利亞,
巴西和新西蘭等提供的動物體.
-
porcine (pig) tissue is also
widely used for producing collagen sheet for a variety of surgical purposes.
豬(豬)
組織也被廣泛用於生產用於多種手術目的膠原薄片.
4.
alternatives using the
patient's own fat, hyaluronic acid, or polyacrylamide gels which are readily available.
使用患者自身的脂肪,
透明質酸,
或polyacrylamide凝膠等做的替代品,
這是容易獲得的.
Bone grafts 骨移植
As the skeleton forms the structure of the body, it is vital that it maintains
its strength, even after breaks and injuries. Collagen is used in bone grafting
as it has a triple helical structure, making it a very strong molecule.
It is ideal for use in bones, as it does not compromise the structural integrity
of the skeleton. The triple helical structure of collagen prevents it from being
broken down by enzymes, it enables adhesiveness of cells and it is important for
the proper assembly of the extracellular matrix.[56]
作為形成身體結構的骨架,
它是重要的,
它保持其強度,
即使在斷裂和損傷之後.
膠原用在骨移植,
是因為它有一個三螺旋結構,
使其成為一個非常強的分子.
它在骨頭的使用是理想的,
因為它不影響骨架的結構完整性.
膠原蛋白的三螺旋結構阻止其被酶所分解,
它使細胞能有附著性,
這對細胞外基質的適當裝配是很重要的.
[56]
Tissue regeneration
組織再生
Collagen scaffolds are used in tissue regeneration, either in sponges, thin
sheets or gels. Collagen has the correct properties for tissue regeneration such
as pore structure, permeability, hydrophilicity and it is stable in vivo.
Collagen scaffolds are also ideal for the deposition of cells, such as osteoblasts and fibroblasts and once inserted, growth is able to
continue as normal in the tissue.[57]
膠原支架以海綿,
薄片或凝膠,
用於組織再生.
膠原具有用於組織再生的正確性質,
如孔隙結構,
滲透性,
親水性和它在體內穩定.
膠原支架對於細胞的沉積也是理想的,
如成骨細胞和成纖維細胞,
而且一旦嵌入後,
能夠如在正常的組織中一樣繼續生長. [57]
Reconstructive surgical uses重建手術用途
Collagens are widely employed in the construction of the artificial skin substitutes used in the management of
severe burns.
These collagens may be derived from bovine, equine, porcine, or even human
sources; and are sometimes used in combination with silicones, glycosaminoglycans, fibroblasts, growth factors and other substances.
膠原蛋白被廣泛應用於在嚴重燒傷管理的人工皮膚替代品的製作.
這些膠原可以從牛,
馬,
豬,
甚至人的來源衍生出來;
並且有時與矽酮,
糖胺聚醣,
纖維母細胞,
生長因子和其他物質的組合使用
Collagen is also sold commercially in pill form as a supplement to aid joint
mobility. However, because proteins are broken down into amino acids before
absorption, there is no reason for orally ingested collagen to affect connective
tissue in the body, except through the effect of individual amino acid
supplementation.
Collagen is also frequently used in scientific research applications for cell
culture, studying cell behavior and cellular interactions with the extracellular
environment.[58].
膠原蛋白以藥片的形式商品化銷售作為補充劑以幫助關節的靈活性.
但是,
因為蛋白質被吸收之前是被分解成氨基酸的,
沒有口服膠原對於影響體內結締組織理由,
除了通過個別氨基酸的補充的效果.
膠原也經常用在細胞培養的科研應用,
研究細胞的行為和與細胞外環境的細胞的相互作用.
[58]
Wound care management uses傷口護理管理使用
Collagen is one of the body’s key natural resources and a component of skin
tissue that can benefit all stages of the wound healing process.
When collagen is made available to the wound bed, closure can occur. Wound
deterioration, followed sometimes by procedures such as amputation, can thus be
avoided.
膠原蛋白是人體的關鍵的自然資源之一,
也是皮膚組織的一個組成部分,
它可以有利於所有階段的傷口癒合過程.
當膠原被提供給傷口位置,
閉合可以發生.
有時隨著過諸如截肢程序的傷口惡化,
因此可以被避免.
Collagen is a natural product, therefore it is used as a natural wound dressing
and has properties that artificial wound dressings do not have.
It is resistant against bacteria, which is of vital importance in a wound
dressing. It helps to keep the wound sterile, because of its natural ability to
fight infection. When collagen is used as a burn dressing, healthy
granulation tissue is able to form very quickly over the
burn, helping it to heal rapidly.[59]
Throughout the 4 phases of wound healing, collagen performs the following
functions in wound healing:
膠原是一種天然產物,
因此它被用來作為一種天然的傷口敷料和具有人工傷口敷料不具有的特性.
它是抗菌的,
這對於傷口敷料是極其重要的.
因為它對抗感染的自然能力,
它有助於保持傷口無菌.
當膠原被用作燒傷敷料,
健康肉芽組織是能夠非常快地形成,
幫助它迅速地癒合.[59]
在整個4階段傷口癒合過程中,
膠原在傷口癒合發揮的的功能如下:
Guiding function: Collagen fibers serve to guide fibroblasts. Fibroblasts
migrate along a connective tissue matrix.
指導作用:膠纖絲做為成纖維細胞的導引.
成纖維細胞沿結締組織基質遷移.
·
Chemotactic properties: The
large surface area available on collagen fibers can attract fibrogenic cells
which help in healing.
趨化特性:膠纖維上的所能得到的大的表面積能吸引纖維化細胞-它有助於癒合的.
·
Nucleation: Collagen, in the
presence of certain neutral salt molecules can act as a nucleating agent causing
formation of fibrillar structures.
A collagen wound dressing might serve as a guide for orienting new collagen
deposition and capillary growth.
核:膠原蛋白,
在某些中性鹽分子的存在時,
可以充當成核劑導致形成纖維狀結構.
膠原的傷口敷料可能作為定向新的膠原沉積和毛細血管生長的導引.
·
Hemostatic properties: Blood platelets interact with the collagen to make a
hemostatic plug.
止血性能:血小板與膠原蛋白相互作用產生了止血塞.
See also另請參見
-
Hydrolyzed collagen, a common form in which collagen is
sold as a supplement.
水解膠原蛋白,
膠原蛋白作為補充銷售的一種常見形式.
-
Animal glue動物膠
-
Gelatine明膠
-
Fibrous
protein纖維蛋白
-
Osteoid,
collagen containing component of bone
骨質,
含膠原蛋白的骨成分
-
Lysyl
oxidase and LOXL1, LOXL2, LOXL3, LOXL4 in collagen formation
Lysyl氧化酶和LOXL1,
LOXL2, LOXL3, LOXL4膠原形成
-
Collagenase,
the enzyme involved in collagen breakdown and remodelling. For more on other proteases that target collagen see The Proteolysis Map
膠原酶,
參與膠原蛋白分解和重構的酶.
欲了解更多關於針對膠原的其他蛋白酶,
請查看蛋白水解地圖
-
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Ehlers-Danlos徵候群
-
Hypermobility Syndrome
過度活動徵候群
-
Sponge - Cell types
海綿
-
細胞類型
-
Drug
discovery and development of MMP inhibitors
藥物發現以及MMP抑製劑的開發
References參考
1.
^ Di Lullo, Gloria A.; Sweeney, Shawn M.; Körkkö, Jarmo; Ala-Kokko, Leena & San
Antonio, James D. (2002). "Mapping the Ligand-binding Sites and
Disease-associated Mutations on the Most Abundant Protein in the Human, Type I
Collagen". J. Biol.
Chem. 277 (6): 4223–4231. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110709200. PMID 11704682.
2.
^ Britannica Concise Encyclopedia 2007
3.
^ Sikorski, Zdzisław E. (2001). Chemical
and Functional Properties of Food Proteins. Boca Raton: CRC Press. p. 242. ISBN 1-56676-960-4.
4.
^ O.E.D. 2nd Edition 2005
5.
^ Müller, Werner E. G. (2003). "The Origin of Metazoan Complexity: Porifera as
Integrated Animals". Integrated
Computational Biology 43 (1): 3–10. doi:10.1093/icb/43.1.3.
6.
^ Wyckoff, R.; Corey, R. & Biscoe, J. (1935). "X-ray reflections of long spacing
from tendon". Science 82 (2121):
175–176.Bibcode:1935Sci....82..175W. doi:10.1126/science.82.2121.175. PMID 17810172.
7.
^ Clark, G.; Parker, E.; Schaad, J. & Warren, W. J. (1935). "New measurements of
previously unknown large interplanar spacings in natural materials". J. Amer. Chem. Soc 57 (8): 1509. doi:10.1021/ja01311a504.
8.
^ Balasubramanian, D . (October 2001). "GNR — A Tribute". Resonance (Indian
Academy of Sciences) 6 (10).
9.
^ Leonidas, Demetres D.; Chavali, GB et al. (2001). "Binding of Phosphate and pyrophosphate ions at the
active site of human angiogenin as revealed by X-ray crystallography". Protein
Science 10 (8): 1669–1676. doi:10.1110/ps.13601.PMC 2374093. PMID 11468363.
10.
^ Subramanian,
Easwara (2001). "Obituary: G.N. Ramachandran". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 8 (6):
489–491.doi:10.1038/88544. PMID 11373614.
11.
^ Fraser,
R. D.; MacRae, T. P. & Suzuki, E. (1979). "Chain conformation in the collagen
molecule". J Mol Biol 129 (3):
463–481.doi:10.1016/0022-2836(79)90507-2. PMID 458854.
12.
^ Okuyama,
K.; Okuyama, K et al. (1981). "Crystal and molecular structure of a
collagen-like polypeptide (Pro-Pro-Gly)10". J Mol Biol 152 (2): 427–443. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(81)90252-7. PMID 7328660.
13.
^ Traub,
W.; Yonath, A. & Segal, D. M. (1969). "On the molecular structure of collagen". Nature 221 (5184):
914–917.Bibcode:1969Natur.221..914T. doi:10.1038/221914a0.
14.
^ Bella,
J.; Eaton, M.; Brodsky, B.; Berman, H. M. (1994). "Crystal and molecular
structure of a collagen-like peptide at 1.9 A resolution". Science 266 (5182):
75–81. Bibcode:1994Sci...266...75B. doi:10.1126/science.7695699. PMID 7695699.
15.
^ to:a b Hulmes,
D. J. & Miller, A. (1979). "Quasi-hexagonal molecular packing in collagen
fibrils". Nature 282 (5741): 878–880.Bibcode:1979Natur.282..878H. doi:10.1038/282878a0. PMID 514368.
16.
^ Jesior,
J. C.; Miller, A. & Berthet-Colominas, C. (1980). "Crystalline three-dimensional
packing is general characteristic of type I collagen fibrils". FEBS Lett 113 (2): 238–240. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(80)80600-4. PMID 7389896.
17.
^ Fraser,
R. D. B. & MacRae, T. P. (1981). "Unit cell and molecular connectivity in tendon
collagen". Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 3(3): 193–200. doi:10.1016/0141-8130(81)90063-5.
18.
^ Fraser,
R. D.; MacRae, T. P.; Miller, A. (1987). "Molecular packing in type I collagen
fibrils". J Mol Biol 193 (1): 115–125.doi:10.1016/0022-2836(87)90631-0. PMID 3586015.
19.
^ Wess,
T. J.; Hammersley, AP et al. (1998). "Molecular packing of type I collagen in
tendon". J Mol Biol 275 (2): 255–267.doi:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1449. PMID 9466908.
20.
^ Raspanti,
M.; Ottani, V.; Ruggeri, A. (1990). "Subfibrillar architecture and functional properties
of collagen: a comparative study in rat tendons". J Anat. 172: 157–164. PMC 1257211. PMID 2272900.
21.
^ Holmes,
D. F.; Gilpin, C. J.; Baldock, C.; Ziese, U.; Koster, A. J.; Kadler, K. E.
(2001). "Corneal collagen fibril structure in three
dimensions: Structural insights into fibril assembly, mechanical properties, and
tissue organization". PNAS 98 (13): 7307–7312. Bibcode:2001PNAS...98.7307H. doi:10.1073/pnas.111150598. PMC 34664. PMID 11390960.
22.
^ Holmes,
D. F.; Kadler, KE (2006). "The 10+4 microfibril structure of thin cartilage
fibrils". PNAS 103 (46): 17249–17254.Bibcode:2006PNAS..10317249H. doi:10.1073/pnas.0608417103. PMC 1859918. PMID 17088555.
23.
^ to:a b c Orgel,
J. P.; Irving, TC et al. (2006). "Microfibrillar structure of type I collagen in situ". PNAS 103 (24): 9001–9005.Bibcode:2006PNAS..103.9001O. doi:10.1073/pnas.0502718103. PMC 1473175. PMID 16751282.
24.
^ Okuyama,
K; Bächinger, HP; Mizuno, K; Boudko, SP; Engel, J; Berisio, R; Vitagliano, L
(2009). "Comment on Microfibrillar structure of type I collagen in situ by Orgel
et al. (2006), Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 103, 9001–9005". Acta
Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 65 (Pt9):
1009–10. doi:10.1107/S0907444909023051. PMID 19690380.
25.
^ Narayanaswamy,
Radhakrishnan; Shanmugasamy, Sangeetha; Shanmugasamy, Sangeetha; Gopal, Ramesh;
Mandal, Asit (2011). "Bioinformatics in crosslinking chemistry of collagen with
selective crosslinkers". BMC 4: 399. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-4-399.
26.
^ to:a b c d e f Szpak,
Paul (2011). "Fish bone chemistry and ultrastructure: implications
for taphonomy and stable isotope analysis". Journal
of Archaeological Science 38 (12): 3358–3372. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2011.07.022.
27.
^ Diegelmann,
Robert. "Collagen Metabolism". Medscape.com. Medscape.
Retrieved 4 December 2014.
28.
^ Gorres,
K. L.; Raines, R. T. (2010). "Prolyl 4-hydroxylase". Crit.
Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 45 (2): 106–24.doi:10.3109/10409231003627991. PMC 2841224. PMID 20199358.
29.
^ Myllylä,
R.; Majamaa, K.; Günzler, V.; Hanauske-Abel, H. M.; Kivirikko, K. I. (1984).
"Ascorbate is consumed stoichiometrically in the uncoupled reactions catalyzed
by propyl 4-hydroxylase and lysyl hydroxylase". J.
Biol. Chem. 259 (9): 5403–5.PMID 6325436.
30.
^ Houck,
J. C.; Sharma, V. K.; Patel, Y. M.; Gladner, J. A. (1968). "Induction of
Collagenolytic and Proteolytic Activities by AntiInflammatory Drugs in the Skin
and Fibroblasts". Biochemical
Pharmacology 17 (10): 2081–2090. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(68)90182-2. PMID 4301453.
31.
^ Al-Hadithy,
H.; Isenberg, DA et al. (1982). "Neutrophil function in systemic lupus erythematosus
and other collagen diseases". Ann
Rheum Dis 41 (1): 33–38. doi:10.1136/ard.41.1.33. PMC 1000860. PMID 7065727.
32.
^ Hulmes,
D. J. (2002). "Building collagen molecules, fibrils, and suprafibrillar
structures". J Struct Biol 137 (1–2):
2–10.doi:10.1006/jsbi.2002.4450. PMID 12064927.
33.
^ to:a b Hulmes,
D. J. (1992). "The collagen superfamily—diverse structures and assemblies". Essays Biochem 27: 49–67.PMID 1425603.
34.
^ Perumal,
S.; Antipova, O. & Orgel, J. P. (2008). "Collagen fibril architecture, domain organization,
and triple-helical conformation govern its proteolysis". PNAS 105 (8):
2824–2829. Bibcode:2008PNAS..105.2824P.doi:10.1073/pnas.0710588105. PMC 2268544. PMID 18287018.
35.
^ Sweeney,
S. M.; Orgel, JP et al. (2008). "Candidate Cell and Matrix Interaction Domains on the
Collagen Fibril, the Predominant Protein of Vertebrates". J
Biol Chem 283 (30): 21187–21197. doi:10.1074/jbc.M709319200. PMC 2475701.PMID 18487200.
36.
^ Twardowski,
T.; Fertala, A. et al. (2007). "Type I collagen and collagen mimetics as angiogenesis
promoting superpolymers". Curr Pharm
Des 13 (35): 3608–3621. doi:10.2174/138161207782794176.
37.
^ Minary-Jolandan,
M; Yu, MF (2009). "Nanomechanical heterogeneity in the gap and overlap regions
of type I collagen fibrils with implications for bone heterogeneity". Biomacromolecules 10 (9):
2565–70. doi:10.1021/bm900519v. PMID 19694448.
38.
^ Ross, M. H. and Pawlina, W. (2011) Histology, 6th ed., Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, p. 218.
39.
^ Sabiston textbook of surgery board review, 7th edition. Chapter 5 wound healing,
question 14
40.
^ Söderhäll,
C.; Marenholz, I.; Kerscher, T.; Rüschendorf, F; Rüschendorf, F.;
Esparza-Gordillo, J.; Mayr, G et al. (2007)."Variants in a Novel Epidermal Collagen Gene (COL29A1)
Are Associated with Atopic Dermatitis". PLoS Biology 5 (9):
e242.doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050242. PMC 1971127. PMID 17850181. |first7= missing |last7= in
Authors list (help)
41.
^ to:a b Mahajan,
VB, Olney, AH, Garrett, P, Chary, A, Dragan, E, Lerner, G, Murray, J & Bassuk,
AG; Olney; Garrett; Chary; Dragan; Lerner; Murray; Bassuk (2010). "Collagen XVIII mutation in Knobloch syndrome with
acute lymphoblastic leukemia".American journal of medical
genetics. Part A 152A (11): 2875–9. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.33621. PMC 2965270.PMID 20799329.
42.
^ Gajko-Galicka,
A (2002). "Mutations in type I collagen genes resulting in
osteogenesis imperfecta in humans". Acta
biochimica Polonica 49 (2): 433–41. PMID 12362985.
43.
^ Horton,
WA, Campbell, D, Machado, MA & Chou, J; Campbell; Machado; Chou (1989). "Type II
collagen screening in the human chondrodysplasias". American
journal of medical genetics 34 (4): 579–83. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320340425.PMID 2624272.
44.
^ Hamel,
BCJ; Pals, G.; Engels, CHAM; Akker, E.; Boers, GHJ; van Dongen, PWJ; Steijlen,
PM (28 June 2008). "Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and type III collagen abnormalities:
a variable clinical spectrum". Clinical
Genetics 53 (6): 440–446.doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.1998.tb02592.x. PMID 9712532.
45.
^ Kashtan, CE (1993) "Collagen IV-Related Nephropathies (Alport Syndrome and Thin Basement Membrane Nephropathy)",
in RA Pagon, TD Bird, CR Dolan, K Stephens & MP Adam (eds), GeneReviews,
University of Washington, Seattle, Seattle WAPMID 20301386.
46.
^ Shuster,
S (2005). "Osteoporosis, a unitary hypothesis of collagen loss in skin and
bone". Medical hypotheses 65 (3):
426–32.doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2005.04.027. PMID 15951132.
47.
^ Fratzl,
P. (2008). Collagen: Structure and Mechanics. New York: Springer. ISBN 0-387-73905-X.
48.
^ Buehler,
M. J. (2006). "Nature designs tough collagen: Explaining the
nanostructure of collagen fibrils". PNAS 103 (33):
12285–12290. Bibcode:2006PNAS..10312285B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0603216103. PMC 1567872. PMID 16895989.
49.
^ Structure of Skin | The Aging Skin[dead link]
50.
^ to:a b Dermal Fillers | The Ageing Skin.
Pharmaxchange.info. Retrieved on 2013-04-21.
51.
^ "Gelatin's Advantages: Health, Nutrition and Safety". gmap-gelatin.com.
52.
^ Walker,
Amélie A. (May 21, 1998). "Oldest Glue Discovered". Archaeology.
53.
^ Ennker,
I. C.; Ennker, JüRgen et al. (1994). "Formaldehyde-free collagen glue in experimental lung
gluing". Ann Thorac
Surg. 57 (6):
1622–1627. doi:10.1016/0003-4975(94)90136-8. PMID 8010812.
54.
^ Trentham,
D.; Dynesius-Trentham, R.; Orav, J.; Combitchi, D.; Lorenzo, C.; Sewell, K.;
Hafler, D. & Weiner, H. (1993). "Effects of Oral Administration of Type II
Collagen on Rheumatoid Arthritis". Science 261 (5119):
1727–1730.Bibcode:1993Sci...261.1727T. doi:10.1126/science.8378772.
55.
^ Schauss,
A., Stenehjem, J., Park, J., Endres, J., and Clewell, A. (2012). "Effect of the
novel low molecular weight hydrolyzed chicken sternal cartilage extract, BioCell
Collagen, on improving osteoarthritis-related symptoms: A randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial". Journal
of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 60 (16):
4096–101. doi:10.1021/jf205295u.PMID 22486722.
56.
^ Cunniffe,
G; F O'Brien (2011). "Collagen scaffolds for orthopedic regenerative medicine". The Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society 63 (4):
66–73. Bibcode:2011JOM....63d..66C. doi:10.1007/s11837-011-0061-y.
57.
^ Oliveira,
S; R Ringshia; R Legeros; E Clark; L Terracio; C Teixeira M Yost (2009). "An improved collagen scaffold for skeletal
regeneration". Journal of Biomedical Materials 94 (2):
371–379. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.32694. PMC 2891373.PMID 20186736.
58.
^ Blow,
Nathan (2009). "Cell culture: building a better matrix". Nature
Methods 6 (8): 619–622. doi:10.1038/nmeth0809-619.
59.
^ Singh,
O; SS Gupta; M Soni; S Moses; S Shukla; RK Mathur (2011). "Collagen dressing versus conventional dressings in
burn and chronic wounds: a retrospective study". Journal
of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery 4 (1):
12–16.doi:10.4103/0974-2077.79180. PMC 3081477. PMID 21572675.
External links外部鏈接
·
12 types of collagen
12類型的膠原蛋白
·
Database of type I and type III collagen mutations
I型和III型膠原基因突變的資料庫
·
Science.dirbix Collagen
膠原蛋白
·
Collagen Stability Calculator
膠原蛋白穩定性的計算器
·
Computer-generated animations of the assembly of Type
I and Type IV Collagens
計算機產生的I型和IV型膠原組裝--動畫
·
Integrin-Collagen interface, PMAP (The Proteolysis Map)—animation
組合蛋白膠原介面, PMAP(蛋白水解地圖)--動畫
·
Integrin-Collagen binding model, PMAP (The Proteolysis Map)—animation
組合蛋白膠原的結合模式, PMAP(蛋白水解地圖)--動畫
·
Collagen-Integrin atomic detail, PMAP (The Proteolysis Map)—animation
膠原--組合蛋白原子細節, PMAP(蛋白水解地圖)--動畫
Translated By :
The Analytical Based Development Center
http://www.chromnet.net/Default.aspx
Email:
service@chromnet.net
LINE:service.abdc, SKYPE: skypeabdc, QQ: qqabdc(2220487599)
Zipcode:407
5th Floor, NO.641, Fu Shun Road, Shi-Tuen District , Taichung City, Taiwan,
R.O.C. 886-4-24628085, FAX:886-4-22569743
|